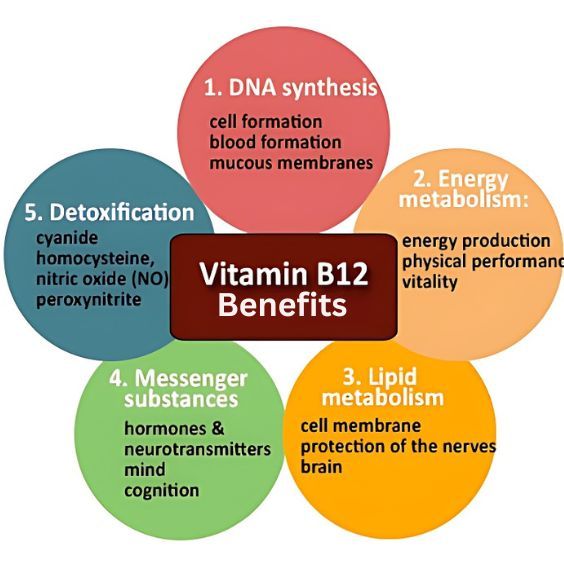
Vitamin B12, a water-soluble vitamin, plays an essential role in our body's ability to function normally. It is vital for the formation of healthy red blood cells, brain and nervous system function, energy production, and the synthesis of DNA. Here we will delve into the benefits of vitamin B12, its food sources, and the consequences of its deficiency.
The Importance of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is crucial for maintaining the health of our nerve cells and the formation of red blood cells. It also helps in the normal function of our brain and nervous system. Lack of this essential vitamin increases the risk of cognitive decline, poor memory performance, and even early-stage dementia. Moreover, it has been linked to cardiovascular disease and age-related macular degeneration.
Studies have shown that vitamin B12, along with folic acid and other B vitamins, can reduce homocysteine levels in the blood. High levels of homocysteine are associated with an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
Vitamin B12 is essential for energy production
Vitamin B12 plays a key role in the production of red blood cells that carry oxygen and nutrients to our bodies. When our body lacks red blood cells, it can cause anemia, resulting in fatigue, and overall weakness.
Hence, it is crucial to ensure that you have an adequate amount of Vitamin B12. A deficiency in this vitamin can also lead to difficulty in breathing and heart palpitations.
It is responsible for maintaining healthy nerves and brain functioning
Vitamin B12 also plays a vital role in protecting our nervous system. It helps in the production of myelin, which is a protective sheath that covers the nerves.
Insufficient levels of this vitamin can result in nerve damage, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. It can also have an impact on your memory and mood, leading to depression and other mental health issues.
Vitamin B12 and Skin Health
Vitamin B12 plays a role in skin health. It helps regulate pigment production in the skin, preventing hyperpigmentation and dark spots. Additionally, vitamin B12 aids in the reproduction of cells, contributing to skin regeneration and the healing of wounds.
Some research indicates that vitamin B12 may play a role in the treatment of certain skin conditions. For instance, a study published in the 'British Journal of Dermatology' found that vitamin B12 could potentially help ease the symptoms of eczema.
However, more research is needed in this area, and it's always best to consult with a healthcare provider or a dermatologist before starting any new supplement regimen for skin health.
Vitamin B12 for Hair Health
Just like skin, hair also benefits from adequate intake of vitamin B12. It plays a significant role in cell production and is essential for hair growth. A deficiency of vitamin B12 can lead to hair loss, as the body won't be able to produce enough healthy hair cells to replace the old ones.
While taking additional B12 supplements may not improve hair growth in people with adequate levels of this vitamin, they could potentially benefit those who are deficient. Before embarking on a new supplement regimen for hair health, it is imperative to seek guidance from a healthcare professional. This step ensures that you make informed decisions and prioritize your well-being.
Vitamin B12 for Eye Health
Vitamin B12 is believed to play a role in eye health, particularly in the optic nerve. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can cause damage to the optic nerve, leading to vision loss. This condition, known as optic neuropathy, can be reversed if the deficiency is treated early.
However, it's important to remember that while vitamin B12 is important for eye health, it's just one piece of the puzzle. Other nutrients like vitamin A, vitamin C, and omega-3 fatty acids also play crucial roles in maintaining good vision.
Vitamin B12 and Immune System
Vitamin B12 plays a vital role in boosting the production of white blood cells, the defenders of our immune system. They're crucial for maintaining a strong and resilient immune system, safeguarding our overall well-being. A deficiency in this vitamin can lead to a decreased ability to fight off infections effectively.
While taking additional vitamin B12 supplements won't necessarily boost your immune system if you're not deficient, maintaining adequate levels of this vitamin is important for overall immune health. As always, it's best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Sources of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is naturally abundant in a diverse range of animal-based foods, such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. However, it is predominantly absent in plant-based foods. Fortunately, individuals adhering to a vegetarian or vegan diet can still obtain this vital nutrient from fortified breakfast cereals and nutritional yeast products.
Animal products are the best food sources of vitamin B12 because the vitamin is bound to the protein in these foods. During digestion, stomach acid and a protein called intrinsic factor help release the vitamin so the body absorbs it.
People who have trouble producing enough intrinsic factors or stomach acid (such as older adults or those taking proton pump inhibitors) may not get enough vitamin B12 from animal foods and may benefit from consuming fortified foods or dietary supplements.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Despite its widespread availability, vitamin B12 deficiency is relatively common, especially among older adults and those with certain health conditions. Pernicious anemia, an autoimmune disease, is a common cause of vitamin B12 deficiency. It occurs when the body lacks an intrinsic factor, a protein needed to absorb vitamin B12.
A deficiency in Vitamin B12 can cause megaloblastic anemia, a condition characterized by abnormally large red blood cells. Symptoms of this deficiency comprise fatigue, weakness, constipation, loss of appetite, weight loss, and nerve damage. Moreover, a severe deficiency can lead to irreversible nerve damage and memory loss.
People following restrictive diets, such as vegan diets, are at a higher risk of vitamin B12 deficiency because plant foods don't contain this nutrient. Therefore, health professionals recommend fortified foods or supplements for these individuals.
Supplementation of Vitamin B12
For those at risk of deficiency, vitamin supplementation can be beneficial. Dietary supplements come in several forms, including tablets, capsules, and injections. They can help to maintain blood levels of vitamin B12 within the normal range.
High doses of vitamin B12 supplements are often recommended to treat pernicious anemia and vitamin B12 deficiency. Very high doses can also reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration, according to the National Institutes of Health.
However, it's important to note that while supplementation can prevent deficiency, it may not improve cognitive function in those without deficiency. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found no difference in cognitive decline between a group given vitamin B12 supplements and a placebo group.
The Recommended Dietary Allowance and Maximum Daily Dose
The recommended dietary allowance for vitamin B12 varies based on age, dietary habits, and other factors. Adults typically need 2.4 micrograms per day, while pregnant women may require more.
The tolerable upper intake level for vitamin B12 has not been established because it has a low potential for toxicity. The body can safely handle very high doses because only a small amount is absorbed, and excess amounts are excreted in the urine.


Vitamin B12 is an essential vitamin that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions. It's found naturally in animal foods and fortified foods, making a balanced diet critical for maintaining adequate levels.
Those at risk of deficiency, such as those on vegan diets or older adults with decreased stomach acid, may benefit from supplements. However, it's always best to consult with health professionals before starting any new dietary regimen.
Remember, while vitamin B12 is essential for our health, it is just one piece of the nutritional puzzle. A balanced diet rich in various nutrients is key to overall health and well-being.