Your gut health plays a pivotal role in your overall well-being. It's not just about digestion, but healthy bacteria are also about nutrient absorption, mental health, immune function, and even the prevention of certain diseases. If you're wondering how to get a healthy gut, this comprehensive guide will provide you with everything you need to know.
Understanding the Importance of Gut Health
The gut, which includes your digestive tract from the small intestine to the large intestine, is home to trillions of bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and other microbes collectively known as the gut microbiome1. A balanced gut microbiome is vital for good health, as it helps the body absorb nutrients, supports a healthy immune system, and even influences mental health.
A healthy gut microbiome is diverse and rich in beneficial bacteria which contribute to good gut health. On the other hand, an unhealthy gut might have less diversity and an overabundance of harmful bacteria, leading to issues like irritable bowel syndrome or inflammatory bowel disease.
The Role of Diet in Achieving a Healthy Gut
One of the best ways to improve your gut health is to follow a balanced diet rich in fermented foods, probiotic foods, and prebiotic foods.
Fermented foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and pickled foods are excellent sources of probiotics – the "good bacteria" that support a healthy gut. Probiotic foods such as these can help repopulate your gut with beneficial bacteria and suppress disease-causing bacteria.
Prebiotic foods, such as bananas, asparagus, and whole grains, provide the fuel that your gut bacteria need to thrive. Incorporating both a probiotic supplement and prebiotic foods into your diet is one way to improve gut health.
On the other hand, ultra-processed foods and certain artificial sweeteners can negatively impact gut health by promoting harmful bacteria and causing intestinal inflammation. A diet rich in plant-based foods and low in processed foods can contribute to a healthier gut.
The Connection Between Gut Health and Overall Health
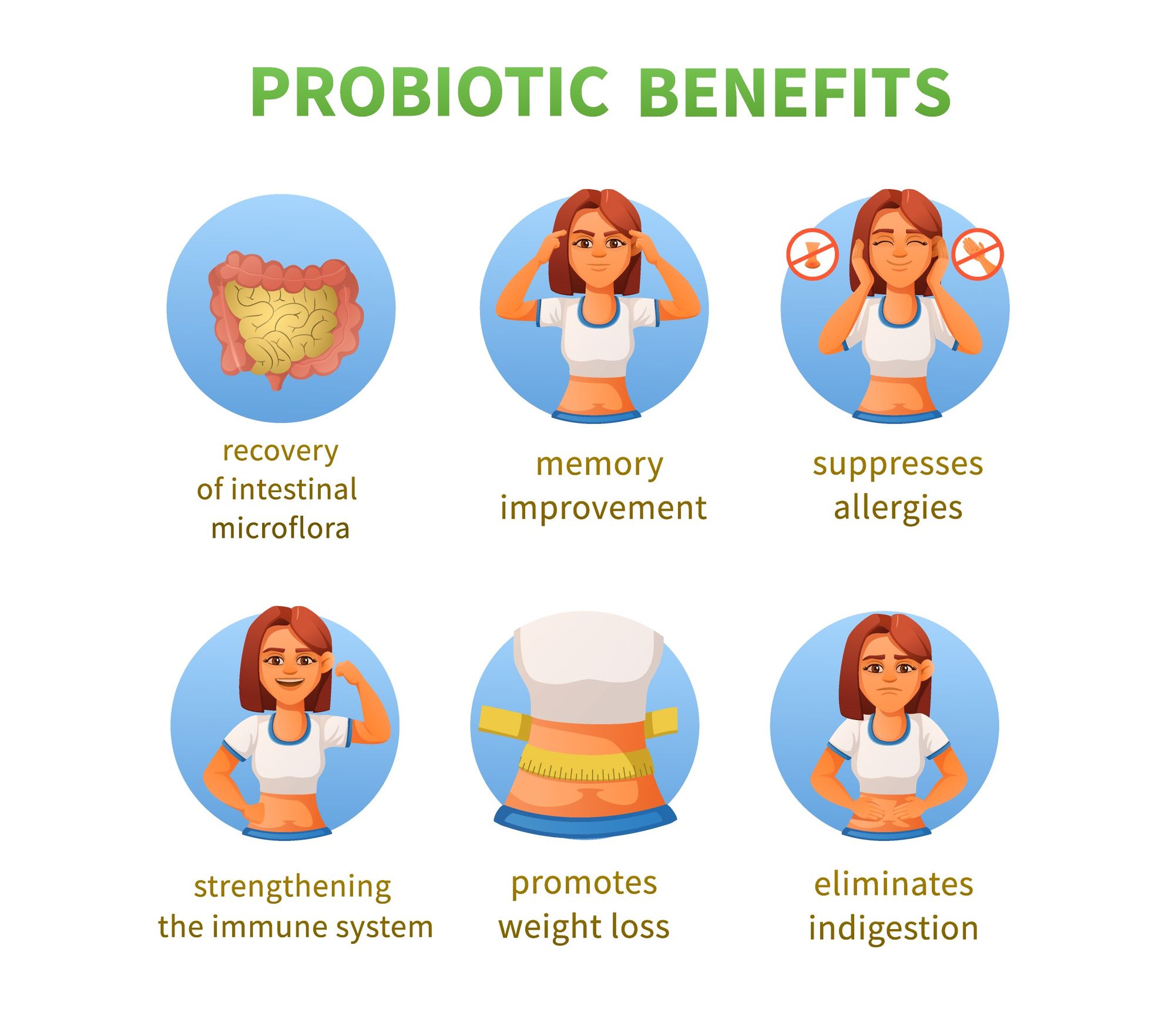
The gut health benefits extend beyond the digestive system. A healthy gut microbiome can support a healthy immune system, as a large portion of the immune system resides in the gut.
Gut health is also linked to mental health through the "gut-brain axis". Research suggests that a healthy gut can have beneficial effects on mood and mental well-being.
Furthermore, gut health can influence metabolic functions. For example, an imbalance in the gut microbiota has been linked to metabolic syndrome, a condition associated with heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
Lifestyle Factors and Gut Health
Diet isn't the only factor influencing gut health. Lifestyle factors like sleep, exercise, and stress management are also important.
Lack of sleep can negatively impact gut health, while regular physical activity promotes a diverse. Managing stress through practices like meditation or yoga can also contribute to good gut health.
The Role of Clinical Nutrition and Medical Guidance
Given the complexity of the gut microbiome and its impact on health, it's crucial to seek medical advice when making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle. A clinical nutritionist or healthcare provider can provide personalized guidance based on your current health conditions, bowel habits, and other factors.
In some cases, probiotic supplements may be recommended. However, these should be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider, as not all supplements are created equal, and some may not be suitable for everyone.

What is a gut microbiome and why is it important?
A gut microbiome refers to the community of trillions of bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and other microbes living in our digestive system, particularly in the large intestine1. These microbes play a crucial role in our health, helping with digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and even mental health2.
A balanced and diverse gut microbiome is essential for good health. It helps the body process food, absorb nutrients, and fight off harmful pathogens. Conversely, an imbalance or lack of diversity in the gut microbiome can lead to various health issues, including digestive disorders, obesity, and even mental health problems.
What's the connection between gut health and overall health?
The gut microbiome impacts more than just our digestive health. A healthy gut microbiome can support a healthy immune system, as a large portion of the immune system resides in the gut7. This means a healthy gut can help protect us from various diseases.
In addition, there's a strong connection between gut health and mental health, often referred to as the "gut-brain axis". Studies suggest that a healthy gut can have beneficial effects on mood and mental well-being. Furthermore, gut health can influence metabolic functions, with imbalances in the gut microbiota being linked to metabolic syndrome, a condition associated with heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
How does lifestyle affect gut health?
Beyond diet, other lifestyle factors like sleep, exercise, and stress management also play a significant role in maintaining gut health. Lack of sleep has been shown to negatively impact gut health, while regular physical activity promotes a.
Chronic stress can also wreak havoc on your gut health, leading to an imbalance in the gut microbiota. Techniques for managing stress, such as meditation and yoga, can help maintain a healthy gut. Thus, a balanced lifestyle is crucial for promoting overall gut health.
Why should I seek medical advice when trying to improve gut health?
Given the complexity of the gut microbiome and its profound impact on overall health, it's essential to seek medical advice when making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle. A healthcare provider or clinical nutritionist can provide personalized guidance based on your current health conditions, bowel habits, and other factors.
In some cases, probiotic supplements may be recommended to support gut health. However, these should be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider, as not all supplements are suitable for everyone, and some may not be as effective as others.
What are probiotics and prebiotics? How do they contribute to gut health?
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are good for your health, especially your digestive system. They are often referred to as 'good' or 'friendly' bacteria because they help keep your gut healthy. Fermented foods like yogurt and sauerkraut are excellent sources of probiotics.
Conversely, prebiotics are a form of dietary fiber that nourishes the beneficial bacteria in your gut. This assists these gut bacteria in creating nutrients essential for your colon cells, contributing to a healthier digestive system. Foods abundant in prebiotic fiber include items like bananas, asparagus, and whole grains.
Yes, there is a significant connection between the gut and the brain, often referred to as the "gut-brain axis". This means that the state of your gut can influence your mental health10. Research suggests that a healthy and diverse gut microbiome can have beneficial effects on mood and mental well-being.
On the flip side, an unhealthy gut has been linked to various mental health issues, including anxiety and depression. Therefore, maintaining good gut health can be a crucial component of mental health care.
What is the impact of processed foods and artificial sweeteners on gut health?
Ultra-processed foods and certain artificial sweeteners can have a negative impact on gut health. They can promote harmful bacteria and cause inflammation in the intestines.
Consuming these foods regularly can lead to an imbalance in the gut microbiota, resulting in a less diverse microbiome. This can contribute to various health issues, including digestive disorders, obesity, and even mental health problems.
How does exercise contribute to gut health?
Regular physical activity has been shown to promote a diverse and healthy gut microbiome. Exercise can alter the composition and function of the gut microbiota, leading to increased diversity and abundance of beneficial bacterial species.
While the exact mechanisms are still being explored, it's believed that exercise can enhance the production of short-chain fatty acids, which are beneficial compounds produced by gut bacteria that play a key role in gut health.
Why is fiber important for gut health?
Dietary fiber is crucial for good gut health because it serves as food for beneficial gut bacteria, known as prebiotics. Consuming a diet high in fiber can help increase the diversity and abundance of beneficial gut bacteria.
Moreover, when gut bacteria ferment dietary fiber, they produce short-chain fatty acids, which have been shown to have numerous health benefits, including anti-inflammatory effects and bowel cancer prevention.

Achieving a healthy gut is a multifaceted process involving diet, lifestyle changes, and sometimes medical intervention. It requires a commitment to consuming a balanced diet rich in plant-based foods, fermented foods, and foods high in fiber, while also managing stress, getting enough sleep, and staying active.
Remember, your gut health is a critical component of your overall health. Taking care of it isn’t just about avoiding digestive issues – it's about promoting good health from the inside out.