Your gut health plays a vital role in your overall well-being. A balanced gut microbiome can influence everything from your immune system to mental health. This article will guide you on how to improve gut health and maintain a healthy gut microbiome.
Understanding the Importance of Gut Health
The digestive tract, often referred to as the gut, is a complex system that does more than just process food. It's home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiota. These include beneficial bacteria that contribute to a healthy immune system, aid in absorbing nutrients, and even impact our mood and mental health1.
Research suggests that a diverse microbiome is key to good health2. Conversely, an unhealthy gut, characterized by an imbalance in the gut microbiota, can lead to various health conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and metabolic syndrome.
The Role of Diet in Gut Health
A diet rich in fermented foods, prebiotic foods, and whole grains can support a healthy gut microbiome. Fermented and probiotic foods like yogurt, kefir, and pickled foods contain probiotics or “good bacteria” that help balance your gut bacteria.
Prebiotic foods such as onions, garlic, and whole grains provide nourishment for these healthy bacteria, promoting their growth and diversity[^5^]. Avoiding ultra-processed foods, which often contain artificial sweeteners and lack nutritional value, is also essential as they can negatively impact gut health.
Lifestyle Factors and Gut Health
Gut health plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. However, most people tend to overlook the impact of lifestyle factors on their gut health. Our gut is home to trillions of microorganisms that contribute to digestion, absorption, metabolism, and immune function. Lifestyle factors such as diet, stress, physical activity, and sleep can significantly influence the composition and function of these microorganisms, thereby impacting gut health. In this post, we will delve deeper into the impact of lifestyle factors on gut health and provide tips to maintain a healthy gut.
Diet:
What we eat plays a significant role in shaping our gut microbiome. A balanced, varied, and fiber-rich diet promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. On the other hand, a diet high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and processed food can disturb the gut microbiome, leading to an increased risk of gut-related diseases. To maintain good gut health, choose whole foods, vegetables, and fruits that are high in fiber, healthy fats, and lean protein. Moreover, promote fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, kefir, and sauerkraut as these foods contain beneficial bacteria.
Stress:
Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health. Stress activates the sympathetic nervous system and triggers the production of cortisol, leading to inflammation and damage to the gut lining. Over time, this can lead to problems like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), leaky gut syndrome, and other digestive disorders. Therefore, it is essential to manage stress effectively to avoid long-term gut health problems. Incorporate relaxing activities like mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing, and getting adequate sleep in your daily routine.
Physical activity:
Exercise can increase gut motility, accelerate digestion, and promote blood flow to the gut. These effects help promote a healthy gut by preventing stagnation and promoting regular bowel movements. Regular physical activity can also promote a healthy weight, which is essential for gut health, as obesity is associated with gut-related diseases. To maintain gut health, incorporate moderate to high-intensity exercise into your routine for at least 30 minutes a day.
Sleep:
Adequate and restful sleep is essential for gut health. During deep sleep, the body repairs and replenishes the gut lining, allowing it to function optimally. Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to inflammatory conditions in the gut as well as an increased risk of gut-related diseases. Therefore, make sure you get at least seven to eight hours of sleep each night to promote gut health.
Why Gut Health Matters
Improving your gut health offers a range of health benefits. A healthy gut microbiome can help you absorb nutrients more efficiently, support immune health, and even regulate blood sugar levels.
The connection between your gut and your immune system
Your gut flora, or microbiome, is home to trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. While the term “bacteria” might have a negative connotation, there are many helpful bacteria in your gut that keep your immune system in check.
When your gut microbiome is unbalanced, harmful bacteria can take over, leading to a weakened immune system and increased vulnerability to illnesses. By maintaining a healthy gut, you’re able to strengthen your immune system and better protect yourself from health threats.
The gut-brain axis
The relationship between your gut and brain is referred to as the “gut-brain axis,” and research has shown that these two organs are closely connected. The gut produces around 90% of the body’s serotonin, a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating mood, appetite, and sleep.
A healthy gut can boost your mental health, while an unhealthy gut has the potential to cause anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders. Additionally, when gut inflammation occurs, it can cause a breakdown in the gut-brain axis and negatively impact your overall health.
Common factors that damage gut health
Certain factors can adversely impact your gut health, including a lack of sleep, unhealthy diets, stress, and overuse of antibiotics. Excessive sugar intake, a diet low in fiber, and consuming processed foods and alcohol are all also harmful to your gut.
How to support gut health
Caring for your gut health involves making healthy lifestyle changes, such as getting enough sleep, reducing stress, and eating a balanced diet. Incorporating fiber-rich foods into your meals, such as leafy greens, nuts, and seeds can also promote gut health.
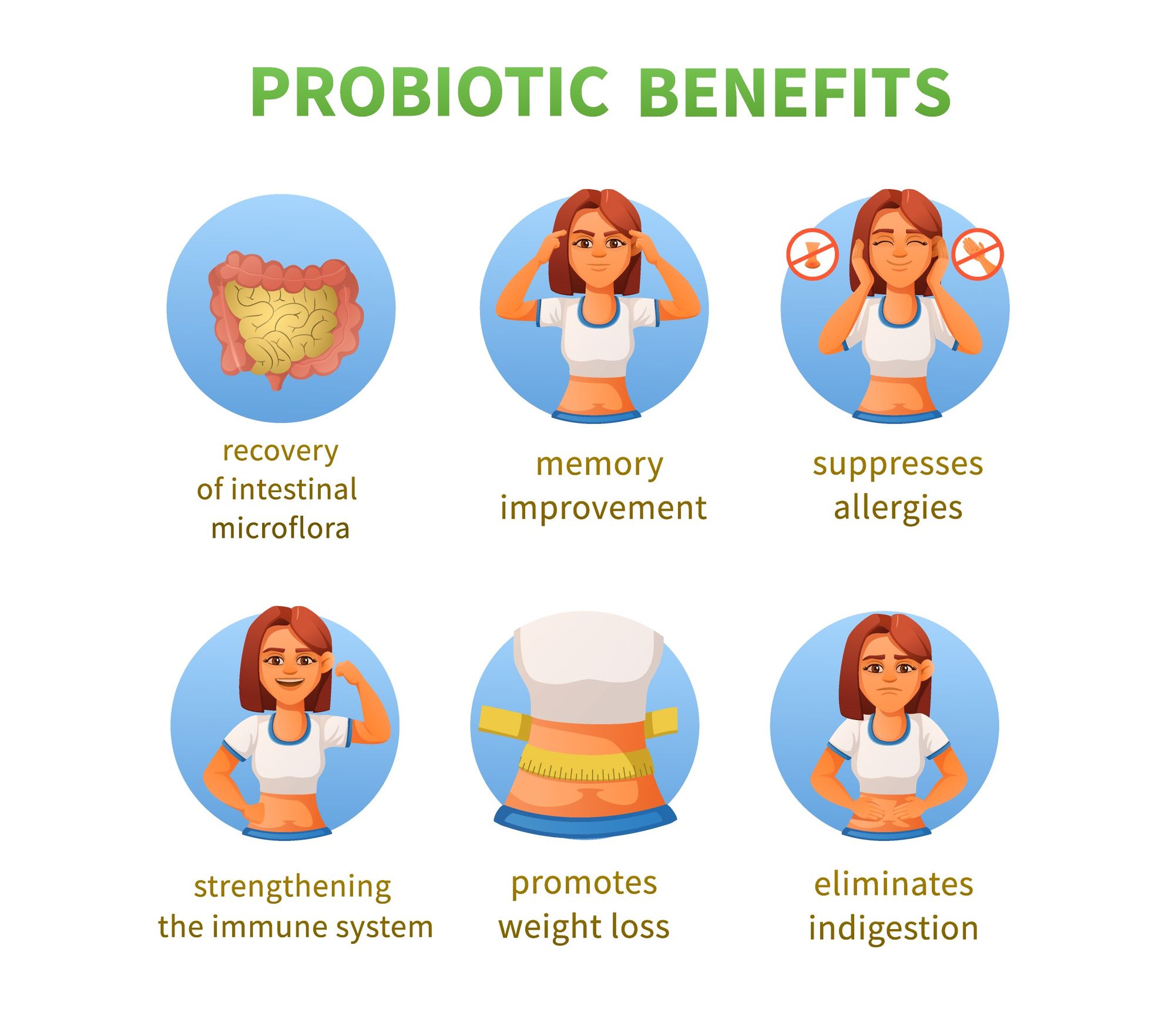
Another great way to support gut health is by taking a daily probiotic supplement. Probiotics help replenish the good bacteria in your gut, improving digestion, absorption of nutrients, and promoting a healthy immune system.
Steps to Improve Gut Health
To improve your gut health, start by incorporating more probiotic and prebiotic foods into your diet. This helps increase the beneficial gut bacteria and encourages a more diverse microbiome.
Next, limit your intake of ultra-processed foods and artificial sweeteners, which can upset the balance of your gut bacteria. Instead, opt for whole foods that are rich in fiber and have high nutritional value.
Regular physical activity is another effective way to enhance gut health. Exercise can boost the diversity of your gut microbiota and contribute to a healthy immune system.
Lastly, don’t underestimate the power of good sleep and stress management. Both can significantly influence your gut health, so it’s important to prioritize these aspects of your lifestyle.

Why is gut health important?
Gut health is crucial because it affects more than just your digestive system. It involves the balance of microorganisms that live in your digestive tract, particularly the gut microbiota, which includes beneficial bacteria. These bacteria play a vital role in several aspects of your health, including your immune system and mental health. They assist in absorbing nutrients from food and can even influence your mood.
Moreover, research suggests that a diverse microbiome contributes to overall good health. On the other hand, an unhealthy gut, characterized by an imbalance in the gut microbiota, can lead to various health conditions. These conditions include inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and metabolic syndrome, all of which could have significant impacts on your quality of life and long-term health.
How does diet affect gut health?
Diet plays a pivotal role in maintaining and improving gut health. Consuming a diet rich in fermented foods, prebiotic foods, and whole grains can help support a healthy gut microbiome. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and pickled foods are rich in probiotics or "good bacteria" that help balance your gut bacteria. Prebiotic foods such as onions, garlic, and whole grains provide nourishment for these beneficial bacteria, promoting their growth and diversity.
On the flip side, ultra-processed foods can negatively impact gut health. These foods often contain artificial sweeteners and lack nutritional value, leading to an imbalance in gut bacteria. Therefore, it is essential to limit the intake of such foods and focus on consuming whole foods that are rich in fiber and nutrients to maintain a healthy gut.
Are lifestyle factors also important for gut health?
Yes, lifestyle factors significantly influence gut health. Regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management can all contribute to maintaining a healthy digestive system. Exercise can boost the diversity of your gut microbiota, while good sleep and stress management can positively impact the balance of bacteria in your gut.
Physical activity enhances the growth and diversity of beneficial bacteria, which in turn contributes to a healthy immune system. Similarly, poor sleep and high stress levels can negatively impact gut health by disrupting the balance of gut bacteria. Therefore, it's crucial to incorporate regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques into your lifestyle for optimal gut health.
What are the health benefits of improving gut health?
Improving gut health offers a wide range of health benefits. A healthy gut microbiome improves nutrient absorption, supports immune health, and helps regulate blood sugar levels. These factors can significantly contribute to overall well-being and prevent various health conditions.
Moreover, the gut health benefits and microbiome diversity have been linked to a reduced risk of diseases such as heart disease and certain types of cancer. There's also a growing body of evidence suggesting a connection between gut health and mental health. Some studies indicate that a balanced gut microbiome could potentially help manage mental health conditions like anxiety and depression, further establishing the importance of improving gut health.
How can I improve my gut health?
Improving gut health involves a combination of dietary changes and lifestyle modifications. Start by incorporating more probiotic and prebiotic foods into your diet to increase the beneficial gut bacteria and encourage a diverse microbiome. Limit your intake of ultra-processed foods and artificial sweeteners, which can upset the balance of your gut bacteria, and opt for whole foods rich in fiber and nutrients.
Regular physical activity is another effective way to enhance gut health as it can boost the diversity of your gut microbiota. Don't underestimate the power of good sleep and stress management, as both can significantly influence your gut health. By making these changes, you can support a healthy gut microbiome and promote your overall health.

In conclusion, improving gut health involves a combination of a well-balanced diet and healthy lifestyle habits. By taking these steps, you can support a healthy gut microbiome and, in turn, promote your overall health.